Corneal Crosslinking in NYC
Corneal Collagen Crosslinking Overview
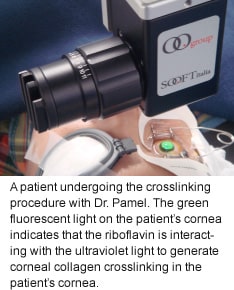
Corneal Crosslinking (CXL), an advanced keratoconus treatment, involves ultraviolet light in combination with topically applied riboflavin (vitamin B) eye drops to increase the crosslinking of the collagen fibers, thereby strengthening the cornea. This procedure has been available internationally since 1998.
Dr. Pamel, a New York City corneal crosslinking provider, was selected as one of 10 principal investigators in the United States to participate in the FDA clinical trials for crosslinking for both keratoconus and post-LASIK ectasia. In many of the peer reviewed articles on corneal crosslinking for keratoconus and post-LASIK ectasia, treatment halted or reversed these conditions.
Corneal Crosslinking Procedure Details
The CXL keratoconus and ectasia treatment involves two parts. In the first part of the treatment, the corneal epithelial layer is removed by Dr. Pamel and the patient receives riboflavin eye drops for 20 minutes to soak the cornea and the anterior chamber. The removal of the epithelium is necessary to allow adequate penetration of riboflavin into the cornea.
Riboflavin serves two functions:
- It interacts with the ultraviolet light to strengthen the collagen in the cornea.
- It blocks the ultraviolet light from penetrating the eye and potentially damaging any intraocular structures.
After the cornea has been soaked with riboflavin, Dr. Pamel inspects your eye to ensure that riboflavin is present within the anterior chamber of the eye.
In the second part of the treatment, the treated eye is exposed to ultraviolet light for 30 minutes, during which time additional riboflavin drops are applied. After the treatment, a contact lens is placed on the eye for approximately three days until the surface heals.
Corneal Crosslinking Recovery
Over the course of the next four weeks, the patient is asked to use antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops to prevent infection and to facilitate healing.
Call Dr. Pamel’s New York / Manhattan corneal collagen crosslinking office today to schedule an appointment to determine if you are a candidate to enroll in the corneal collagen crosslinking clinical trial.
FAQ Regarding Corneal Collagen Crosslinking in New York
What is crosslinking?
Collagen crosslinking is a treatment to strengthen the cornea in patients with keratoconus and post-LASIK/PRK ectasia by using riboflavin in combination with ultraviolet light. The riboflavin interacts with the ultraviolet light to form crosslinks between the collagen fibers in the cornea, thereby strengthening the cornea. In international studies, this process has been shown to stop the progression of keratoconus in over 95 percent of patients. In a majority of keratoconus patients, this treatment can reverse the process, resulting in better vision.
When was crosslinking first performed?
Crosslinking has been performed internationally since 1998, and there are numerous peer reviewed articles in the medical literature on this treatment for keratoconus and post-LASIK ectasia.
How effective is corneal collagen crosslinking?
In several studies, the progression of keratoconus was stopped in more than 95 percent of patients with the corneal crosslinking treatment, and 60-70 percent of those patients experienced a flattening of the cone by up to 1-2 diopters.
Does the crosslinking procedure improve vision in patients with keratoconus and post-LASIK ectasia?
Some reports indicate that best corrected and uncorrected vision improves slightly following corneal collagen crosslinking in patients with keratoconus and post-LASIK ectasia. However, the goal of the treatment is to prevent the progression of the disease.
Does the crosslinking treatment need to be repeated?
Most studies indicate that patients respond to a single crosslinking treatment, which can continue to have an effect on the cornea for 5 years or longer. The data on repeat crosslinking treatments is limited.
Can crosslinking be performed without removal of the corneal epithelium (the outer layer of the cornea)?
For riboflavin to penetrate the cornea, the outer epithelial layer must be removed. While there are some reports of success with crosslinking when the epithelium is left on, no FDA clinical trials to date have shown this to be a safe and effective treatment for keratoconus or post-LASIK ectasia. It is well known that the riboflavin molecule does not penetrate the intact epithelium. However, in the future there may be ways of formulating the riboflavin with other molecules to allow it to penetrate the epithelium so that removal is not necessary.
Can LASIK be performed with corneal collagen crosslinking?
LASIK is contraindicated in patients with keratoconus even after crosslinking. Internationally, several studies have shown that treating patients who have been crosslinked with photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) can improve vision and possibly delay the need for a corneal transplant. However, the available laser technology in combination with crosslinking has not been yet been approved by the FDA.As a skilled corneal crosslinking New York City provider, Dr. Gregory Pamel has been selected as a principal investigator for an FDA corneal crosslinking trial. Call to schedule your consultation today to see if you’re a candidate for the trial.